Released September 8, 1998, AMR is short for audio/modem riser and allows OEMs to make one card with the functionality of either a Modem or audio or both as one card. This specification allows for the motherboard to be manufactured at a lower cost and free up industry standard expansion slots in the system for other additional plug-in peripherals.
The audio/modem riser, also known as an AMR , is a riserexpansion slot found on the motherboards of some Pentium III, Pentium 4, Duron, and Athlonpersonal computers. It was designed by Intel to interface with chipsets and provide analog functionality, such as sound cards and modems, on an expansion card.[1]
Technology[edit]
Physically, it has two rows of 23 pins, making 46 pins total.[2] Three drawbacks of AMR are that it eliminates one PCI slot, it is not plug and play, and it does not allow for hardware accelerated cards (only software-based).[1]
Technologically, it has been superseded by the Advanced Communications Riser (ACR) and Intel's own Communications and Networking Riser (CNR). However, riser technologies in general never really took off. Modems generally remained as PCI cards while audio and network interfaces were integrated on to motherboards.
See also[edit]
Amr Slot To Provide Sound Functions Chart
- Advanced Communications Riser (ACR)
- Communications and Networking Riser (CNR)
References[edit]
- ^ ab'Definition of riser card'. PC Magazine. Retrieved May 2, 2016.
- ^'Audio Modem Riser (AMR)'. Techopedia. Retrieved May 2, 2016.
External links[edit]
- 'Audio/Modem Riser Specification'(PDF). Revision 1.01. Intel. September 10, 1998.
Communications and networking riser (CNR) is a slot found on certain PC motherboards and used for specialized networking, audio, and telephony equipment. A motherboard manufacturer can choose to provide audio, networking, or modem functionality in any combination on a CNR card. CNR slots were once commonly found on Pentium 4-class motherboards, but have since been phased out in favor of on-board or embedded components.
Technology[edit]
Physically, a CNR slot has two rows of 30 pins, with two possible pin configurations: Type A and Type B, each with different pin assignments. CNR Type A uses 8-pin PHY interface, while Type B uses 17-pin media-independent interface (MII) bus LAN interface. Both types carry USB and AC'97 signals.
Amr Slot To Provide Sound Functions Pdf
As with AMR, CNR had the cost savings potential for manufacturers by removing analog I/O components from the motherboard. This allowed the manufacturer to only certify with the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for the CNR card, and not the entire motherboard. This resulted in a quicker production-to-market time for new motherboards, and allowed mass-production of CNR cards to be used on multiple motherboards.
The ACR slot was a competing specification developed by a group of third-party vendors. Its principal advantage over CNR was the backwards-compatible slot layout which allowed it to use both AMR and ACR cards. The same group also developed a physically smaller version, the MDC.
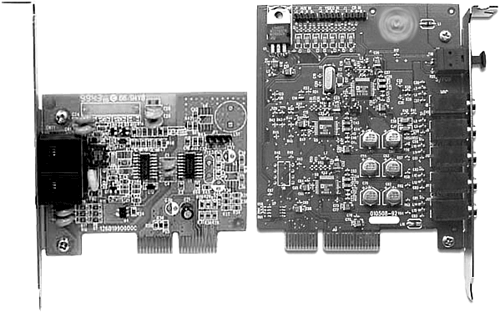
History[edit]

Intel developed the CNR slot to replace its own audio/modem riser (AMR) technology, drawing on two distinct advantages over the AMR slot it replaced; CNR was both capable of being either software based (CPU-controlled) or hardware accelerated (dedicated ASIC), and was plug-and-play compatible. On some motherboards, a CNR slot replaced the last PCI slot, but most motherboard manufacturers engineered boards which allow the CNR and last PCI slot to share the same space.
With the integration of components such as ethernet and audio into the motherboard, the CNR is obsolete, and is not found on PC motherboards anymore.
See also[edit]
- Advanced Communications Riser (ACR)
- Audio/modem riser (AMR)
- Mobile daughter card (MDC)